Understanding the different levels and types
What are Electronic Signatures?
Anyone new to this area can be easily confused about what constitutes an electronic signature and how different types of e-signatures compare in terms of evidential power and legality.
At a basic level any mark on an electronic document can be used to capture the signer’s intent to approve or accept the contents of that document. The form of the “mark” or how it was created is not important. What is important is proving who made the mark and that the document was not changed subsequently.

Electronic signatures
are categorised as
Click-to-Sign SignaturesBasic Electronic Signatures
Advanced Electronic SignaturesQualified Signatures
These signature types and the level of security they provide are explained in more detail below.
Download our free Guide to choosing the right type of e-signature

Electronic signatures are categorized as
Click-to-Sign Signatures
Basic Electronic Signatures
Advanced Electronic Signatures
Qualified Signatures
These signature types and the level of security they provide are explained in more detail below.
Download our free Guide to choosing the right type of e-signature
Click-to-Sign Signatures
These include tick boxes, e-squiggles, scanned images, and typed names. In this category of signature there is no cryptographic protection of the document. So such signatures are not enough to provide strong evidence of who signed or even to protect the document from subsequent change. They can be easily cut/pasted from one document to another. We do not recommend the use of such signatures on their own.


Basic Electronic Signatures
These involve the signer applying their hand-signature mark on the document and then this being protected with a cryptographic digital signature. With basic e-signatures, the crypto digital signature is created using a server-held signing key, e.g. belonging to the service provider organisation, hence we refer to this as a “witness” digital signature. In SigningHub this witness digital signature is applied every time an e-signature mark is applied by the user and cryptographically binds this mark to the document and protects the document from any subsequent changes, thereby ensuring data integrity. This is a long-term signature that includes a trusted timestamp.
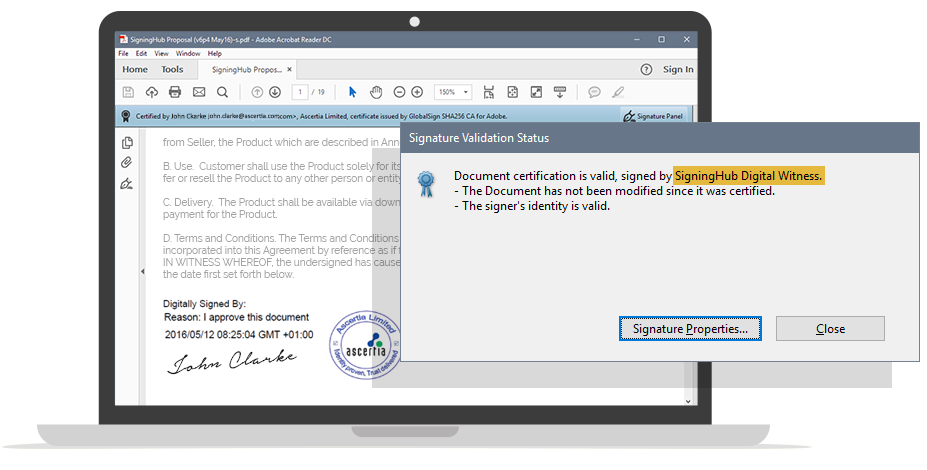
Normally basic e-signatures may or may-not require the user to be registered and their identity validated as a part of this. Regardless of whether or not users are registered with basic e-signatures the signer’s identity is not verifiable directly from the signed document.
Advanced and Qualified eSignatures
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are fully supported in SigningHub. AES and QES provide the highest level of trust and assurance because these use unique signing keys for every signer. This directly links the user’s identity to the signed document such that anyone can verify it on their own using an industry standard PDF reader. Note technically these are also referred to as “digital signatures” rather than “e-signatures”.
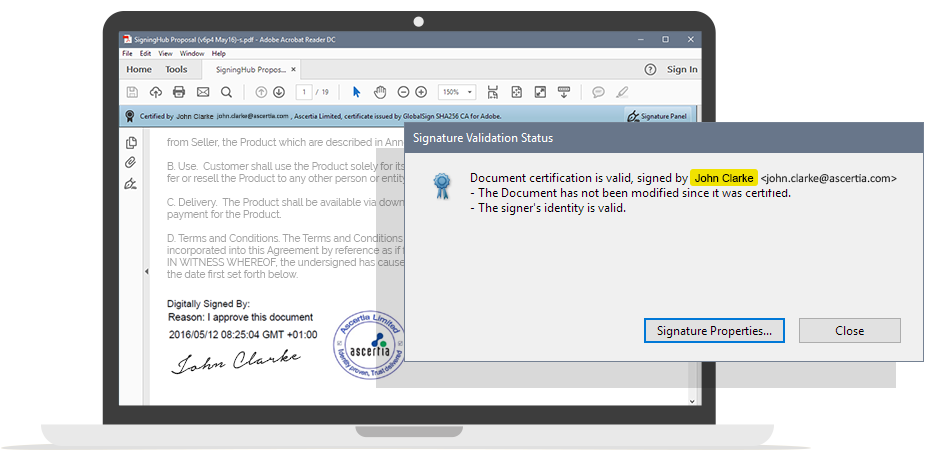
Furthermore, as the signer has sole control of their unique private signing key this ensures non-repudiation, i.e. even the service provider cannot be held responsible for creating the signature. SigningHub complies with eIDAS regulations for AES and QES using locally held credentials, such as a National eID card, or importantly remote signing where the user’s key is held securely, server-side. Remote signing has many benefits including the ability to sign from any machine without use of specialist devices like smartcards, hardware tokens and readers.
The advantage of using AES/QES is that they show exactly who signed the document.
QES are a more trusted version of AES because they require the highest levels of security for the protection of the user’s signing key and also a formal registration process for the user to verify their identity by a qualified Certificate Authority. From a legal perspective QES can be considered even stronger than handwritten signatures as the burden of proof shifts to the signer to prove that they did not sign!
Comparing different types of Electronic Signatures
“Click to Sign”
Basic e-Signatures
Advanced eSignatures
Qualified eSignatures
User Authentication
User Consent
User’s Signature Mark
Document Integrity
Bind Signer’s ID to Doc
Certify Signature
Embedded Evidence
Long Term Verifiability
Audit Information
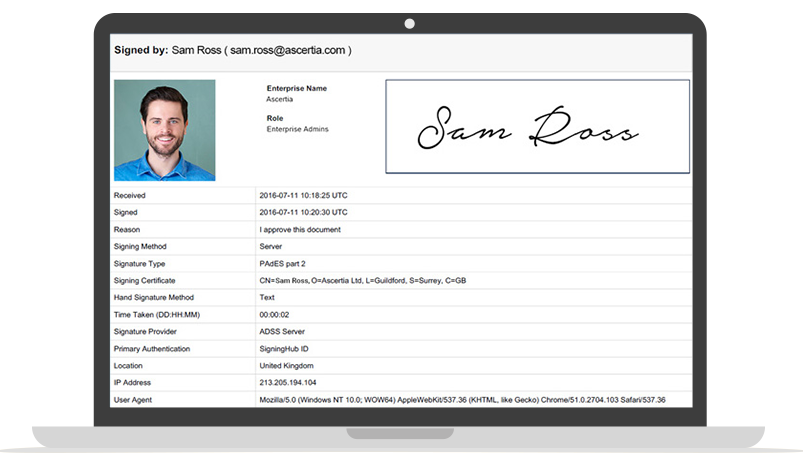
In addition to the evidence provided by the e-signature itself, SigningHub also provides additional evidence in the form of detailed audit information on all user actions that affect a document. This is available on screen and also as a digitally signed Workflow Evidence Report (PDF), which is made available to provide clear evidence of actions, at precise dates/times, IP addresses, authentication mechanisms, legal notices and signatures applied.

The transition to SigningHub’s e-signature solution has been very smooth. It’s really improved our signing process and made it much more efficient. It was standard for contracts to take a few days to come back but now it takes just a few hours.

Helen Wheeler
Traffic Coordinator at Somo

The transition to SigningHub’s e-signature solution has been very smooth. It’s really improved our signing process and made it much more efficient. It was standard for contracts to take a few days to come back but now it takes just a few hours.

Helen Wheeler
Traffic Coordinator at Somo